food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome in adults
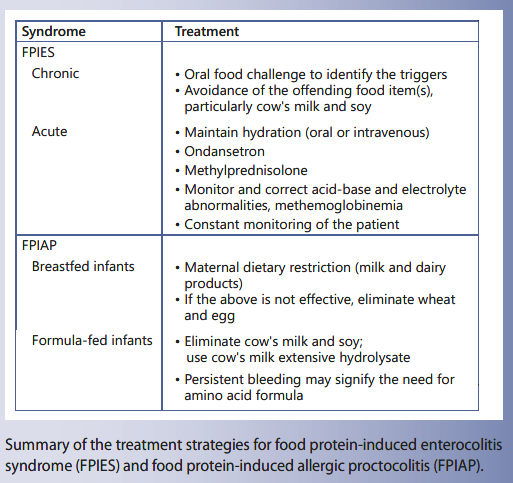
Usual symptoms include vomiting diarrhoea lethargy and in some cases hypovolemic shock and metabolic acidosis. Clinical manifestations of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome.
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults.

. Much like other food allergies FPIES allergic reactions are. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. Changes in blood pressure and body temperature.
Epub 2012 Jul 24. The underlying pathogenic mechanism of FPIES has yet to be elucidated thus disease-specific diagnostic biomarkers have yet to be determined and an oral food challenge. Diarrhea that begins after vomiting.
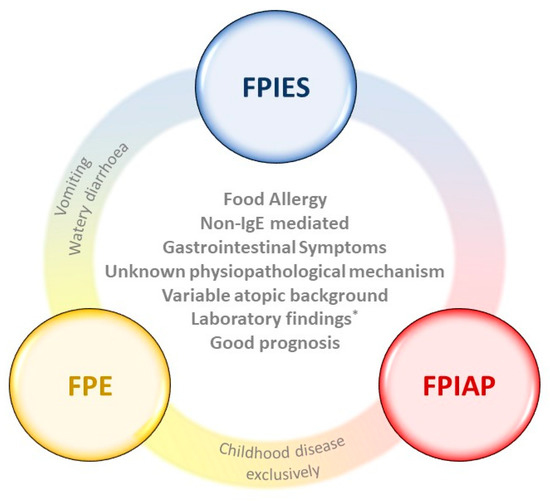
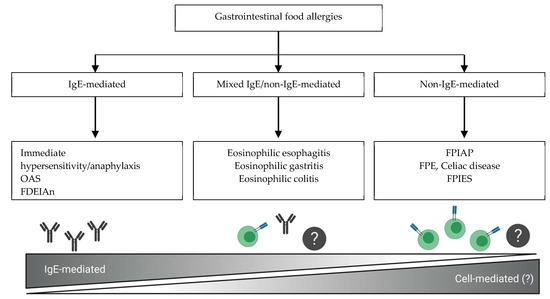
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a delayed non-IgE mediated gut allergic reaction to a foods usually presenting in the first two years of life with an estimated incidence in this age group of 1 in 7000 children. Food-protein induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated reaction affecting predominantly infants and children. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. Mane SK Bahna SL. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. FPIES can occur in adults although this is uncommon. Background Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
FPIES manifests in infants as profuse repetitive vomiting and lethargy. Individuals with FPIES experience profuse vomiting and diarrhea that usually. FPIES has mainly been documented in young infants but can exist in older children and adults.
Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. Objective To describe the clinical characteristics prognosis and associated factors in adult FPIES. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon and potentially severe non-IgE-mediated food allergy.
A 10-year prospective study was conducted in the Allergy Section of Alicante General Hospital in adults diagnosed. Fernandes BN Boyle RJ Gore C Simpson A Custovic A. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy primarily diagnosed in infancy but has also been reported in older children and adults.
We aim to review the recent literature and to provide an update on diagnosis and management of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES and food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in adults is being increasingly recognized. In recent years new-onset adult FPIES has been recognized.
1 In about 1520 of the reactions severe dehydration with hypotension and metabolic. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic. Some people develop both FPIES and an IgE-mediated type of reaction to the same food and having FPIES can increase a persons risk of also developing IgE-mediated food allergies.
Li Andrew Wong-Pack Andrea Leilani Macikunas Harold Kim Allergy Asthma Clinical Immunology volume 16 Article number. Adult cases have been recently reported but are rare A majority of cases occur during infancy particularly with the early introduction of additional foods. However little is known about its characteristics.
Acute FPIES reactions typically present with delayed repetitive vomiting lethargy and pallor within 1 to 4 hours of food ingestion. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. Authors Bryan N Fernandes.
The peer-reviewed articles indexed in PubMed have been reviewed. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children.
In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. J Allergy Clin Immunol. What are the symptoms of FPIES.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis-like syndrome in a population of adolescents and adults caused by seafood J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in adults is being increasingly recognized. It is often caused by cows milk or soy proteins but may also be triggered by the ingestion of other solid.
PDF Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. To describe the clinical characteristics prognosis and associated factors in adult FPIES. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol.
Symptoms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can vary from child to child and in severity. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults J Allergy Clin Immunol. However little is known about its characteristics.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that manifests with repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 hours following food ingestion frequently accompanied by pallor lethargy and may be followed by diarrhea within 68 hours. Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion Daniel H. Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion.
1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation.
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Study Characterizes Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome In Adults

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Classification Scheme Of Fpies Fpies Food Protein Induced Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Fpies In Babies Symptoms Risk Factors And More
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Dr Costa Private Children S Allergy Clinic

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Foods Commonly Implicated In Food Protein Induced Enteropathy And Their Download Table